Articles of confederation vs constitution answer key – Embark on an enlightening journey into the realm of Articles of Confederation vs. Constitution. This comprehensive guide unveils the intricacies of these foundational documents, delving into their historical context, structural differences, and profound impact on the United States.
From the Articles of Confederation’s loose confederation to the Constitution’s robust central government, this exploration unravels the evolution of American governance. Discover the contrasting systems of representation, voting, and federal powers that shaped the nation’s destiny.
Historical Context: Articles Of Confederation Vs Constitution Answer Key
The Articles of Confederation, adopted in 1781, established the United States as a loose confederation of states after the American Revolution. Due to the states’ fear of a strong central government, the Articles granted limited powers to the federal government and left most authority to the individual states.
However, the Articles proved ineffective in addressing the nation’s economic and foreign policy challenges, leading to a constitutional convention in 1787.
The Constitution, ratified in 1788, replaced the Articles of Confederation and created a stronger central government with expanded powers. It established a system of checks and balances among the three branches of government and provided for a more representative system of government through the Electoral College and bicameral legislature.
Structural Differences
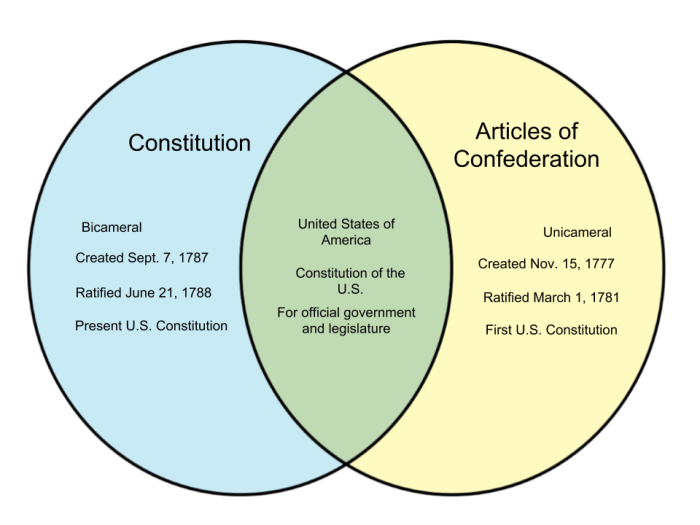
The Articles of Confederation established a unicameral legislature, the Continental Congress, in which each state had one vote regardless of its population. The Constitution, on the other hand, created a bicameral legislature consisting of the House of Representatives and the Senate, with representation based on population in the House and equal representation for each state in the Senate.
The Articles of Confederation also established a weak executive branch with no independent authority. The Constitution, however, created a strong executive branch headed by the President, who has the power to veto legislation, appoint judges, and command the armed forces.
Powers of the Federal Government
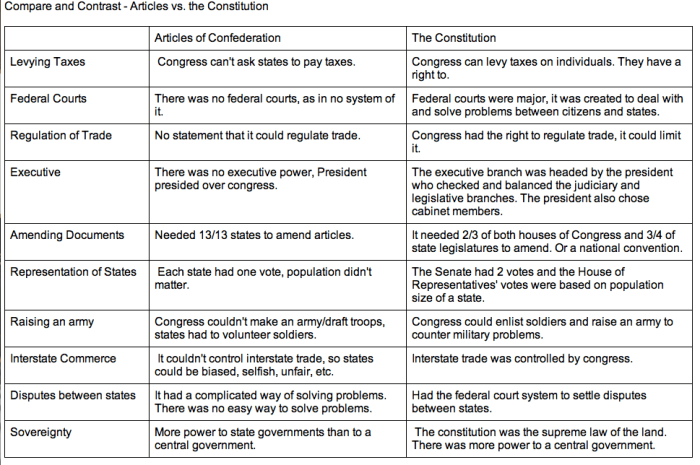
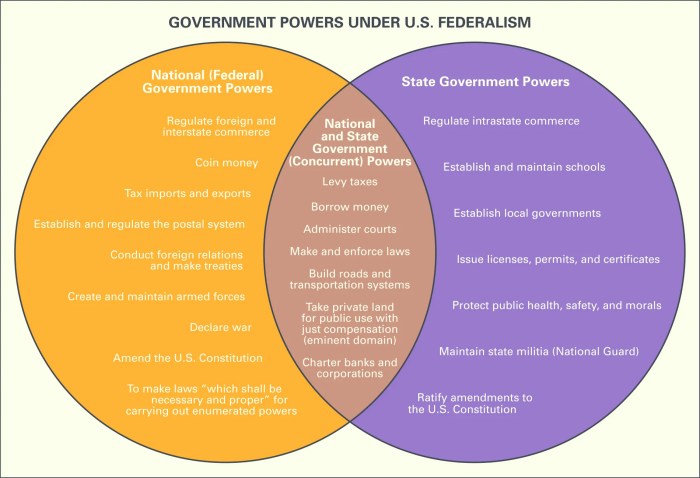
The Articles of Confederation granted the federal government very limited powers, including the authority to declare war, raise armies, and conduct foreign policy. The Constitution, however, expanded these powers significantly, giving the federal government the power to regulate commerce, raise taxes, establish a national bank, and declare war.
The Constitution also established a system of checks and balances among the three branches of government to prevent any one branch from becoming too powerful. For example, the President can veto legislation passed by Congress, but Congress can override the veto with a two-thirds vote.
Representation and Voting
Under the Articles of Confederation, each state had one vote in the Continental Congress, regardless of its population. This system gave small states a disproportionate amount of power compared to larger states.
The Constitution established a more representative system of government through the Electoral College and the bicameral legislature. The House of Representatives is based on population, giving larger states more representation. The Senate, on the other hand, provides equal representation for each state, ensuring that smaller states have a voice in the federal government.
Amendments and Ratification
The Articles of Confederation required unanimous approval from all states to amend the document. This made it extremely difficult to make changes, as even one state could block an amendment.
The Constitution, on the other hand, can be amended with a two-thirds vote of both the House of Representatives and the Senate, followed by ratification by three-fourths of the states. This process is still difficult, but it is much easier than the process for amending the Articles of Confederation.
Legacy and Impact

The Articles of Confederation proved to be ineffective in addressing the challenges facing the United States in the late 18th century. The weak central government and the lack of a national currency and taxation system led to economic instability and foreign policy failures.
The Constitution, on the other hand, has been a successful framework for the United States government for over 200 years. It has allowed the United States to grow into a powerful and prosperous nation and has provided a stable and flexible system of government that has adapted to meet the challenges of a changing world.
FAQ Section
What were the key differences between the Articles of Confederation and the Constitution?
The Articles of Confederation established a loose confederation of states with limited federal power, while the Constitution created a stronger central government with expanded powers.
How did the Articles of Confederation handle representation and voting?
Under the Articles of Confederation, each state had one vote in Congress, regardless of its population.
What is the process for amending the Constitution?
Amendments to the Constitution require a two-thirds vote of both houses of Congress and ratification by three-fourths of the states.
