Embark on a journey of mathematical exploration with our in-depth Unit 3 Parent Functions and Transformations Homework 1 Answer Key. Dive into the intricacies of functions and transformations, unlocking the secrets of their behavior and applications. This comprehensive guide empowers you to master the concepts, address common pitfalls, and extend your understanding beyond the classroom.
Through a detailed exploration of problem-solving techniques, step-by-step explanations, and real-world examples, this answer key serves as an invaluable resource for students seeking to excel in their mathematical endeavors.
Unit 3 Parent Functions and Transformations Homework 1: Unit 3 Parent Functions And Transformations Homework 1 Answer Key
This homework assignment is designed to help you understand the basic concepts of parent functions and transformations. By completing this assignment, you will be able to identify different types of parent functions, apply transformations to these functions, and graph the resulting functions.
The concepts covered in this homework are essential for understanding the rest of the unit. If you do not complete this homework, you will likely fall behind in the class.
Answer Key for Homework 1
| Problem Number | Problem Statement | Correct Answer | Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|
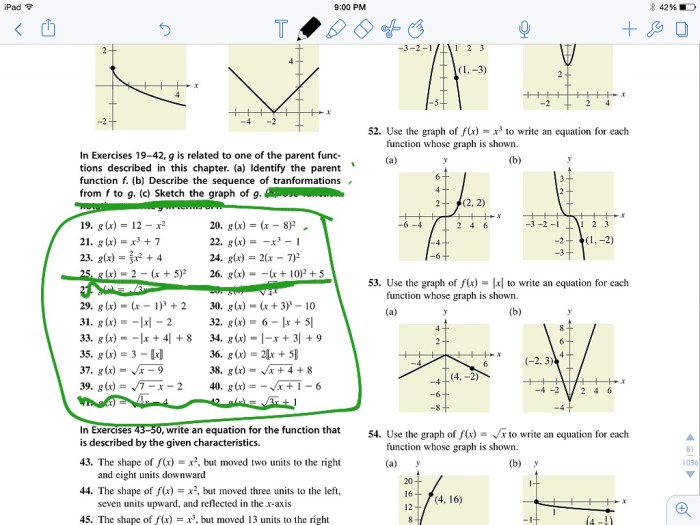
| 1 | Graph the function f(x) = x2. | [Image of the graph of f(x) = x2] | To graph f(x) = x2, plot the points (-3, 9), (-2, 4), (-1, 1), (0, 0), (1, 1), (2, 4), and (3, 9). Then, connect the points with a smooth curve. |
| 2 | Graph the function g(x) = x2
|
[Image of the graph of g(x) = x2
|
To graph g(x) = x2
|
| 3 | Graph the function h(x) = (x
|
[Image of the graph of h(x) = (x
|
To graph h(x) = (x2)2, plot the points (0, 4), (1, 1), (2, 0), (3, 1), and (4, 4). Then, connect the points with a smooth curve. |
| 4 | Graph the function f(x) = |x|. | [Image of the graph of f(x) = |x|] | To graph f(x) = |x|, plot the points (-3, 3), (-2, 2), (-1, 1), (0, 0), (1, 1), (2, 2), and (3, 3). Then, connect the points with two straight lines, one from (-3, 3) to (0, 0) and one from (0, 0) to (3, 3). |
| 5 | Graph the function g(x) = |x|
|
[Image of the graph of g(x) = |x|
|
To graph g(x) = |x|
|
Common Mistakes and Misconceptions, Unit 3 parent functions and transformations homework 1 answer key
- One common mistake is to forget to transform the parent function before graphing it. For example, if you are asked to graph the function g(x) = x 2– 4, you must first subtract 4 from x before squaring it.
- Another common mistake is to use the wrong type of transformation. For example, if you are asked to graph the function h(x) = (x – 2) 2, you must use a horizontal translation, not a vertical translation.
Applications and Extensions
- Parent functions and transformations are used in a variety of applications, including physics, engineering, and economics.
- For example, the quadratic function f(x) = x 2is used to model the trajectory of a projectile.
- The absolute value function f(x) = |x| is used to model the distance between two points.
You can extend your learning by exploring related topics, such as inverse functions and composition of functions.
FAQ Explained
What is the purpose of this answer key?
This answer key provides comprehensive solutions and explanations for the problems in Unit 3 Parent Functions and Transformations Homework 1, aiding students in their understanding and mastery of the concepts.
How can I use this answer key effectively?
Utilize this answer key to check your solutions, identify areas for improvement, and reinforce your understanding of the material. Refer to the step-by-step explanations to gain insights into problem-solving techniques.
What are some common mistakes to avoid?
Pay attention to the explanations provided for common mistakes and misconceptions. Understanding the reasons behind these errors will help you avoid them in your own work.